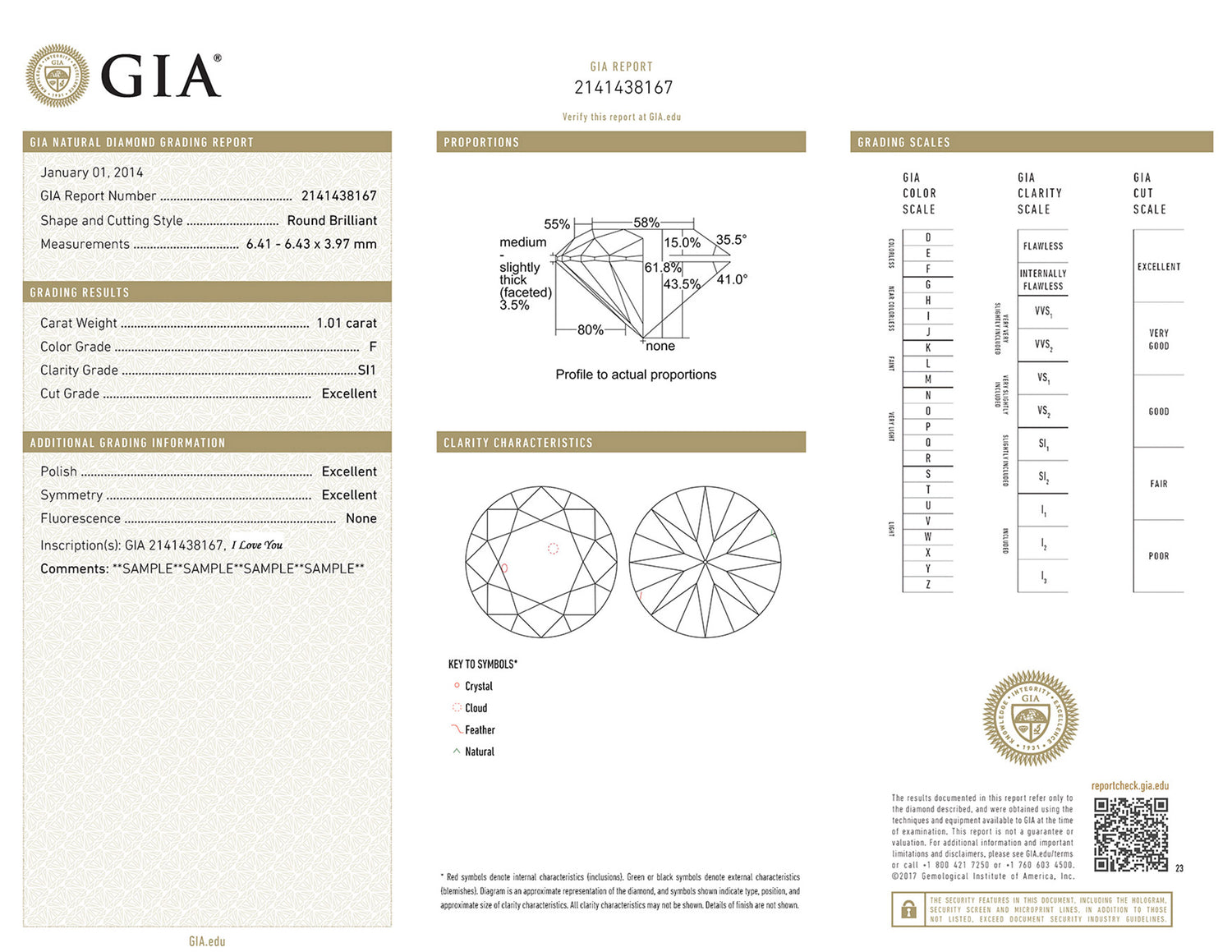
Essential knowledge for distinguishing diamond grades! How to read a GIA diamond 4C watch?
Understanding the basics of diamond grading can help you make informed decisions based on your needs when purchasing diamonds. This article introduces the GIA diamond 4Cs standard and covers seven grading methods, including fluorescence, polish, and symmetry. Quickly mastering this information will allow you to easily understand GIA certificates and choose the diamond that best suits your needs.
How to quickly understand the GIA diamond 4Cs chart? What are the 7 major diamond grading methods?
The GIA 4Cs are the four main standards for evaluating diamond quality, established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).
⬧ Carat (weight): The weight of a diamond. 1 carat equals 0.2 grams. ⬧ Color (color): The color grade of a diamond, from D (colorless) to Z (pale yellow).
⬧Clarity: The internal and external flaws of a diamond, graded from FL (Flawless) to I3 (Significantly Flawed)
⬧ Cut: The proportions and craftsmanship of a diamond's cut, affecting its brilliance and fire; grades range from Excellent to Poor.
❅The quality and value of a diamond are determined by these four criteria together.
2. Color



The Hearts and Arrows pattern is primarily found in finely cut round brilliant diamonds. When viewed from above, eight symmetrical arrows are visible; when viewed from below, eight symmetrical heart shapes appear. This visual effect is produced by the diamond's highly symmetrical interior and precise cutting angles, maximizing its brilliance and fire.  ❅ The first part lists the GIA 4Cs, the four major diamond grading standards. Adding the three diamond characteristics mentioned later makes a total of seven diamond grading methods.
❅ The first part lists the GIA 4Cs, the four major diamond grading standards. Adding the three diamond characteristics mentioned later makes a total of seven diamond grading methods.
5. Diamond polish
The polish of a diamond refers to the smoothness of its surface, which significantly affects its brilliance and fire. In diamond grading, it is classified into five grades: EX, VG, G, F, and P.
- Excellent (EX): The surface is extremely smooth, with no visible polishing marks. This is the highest polish rating, representing the diamond's optimal luster and brightness.
- Very Good (VG): The surface has very few polishing marks, but these are barely noticeable under normal viewing conditions. The diamond's luster and brilliance remain excellent.
- Good (G): There are some polishing marks on the surface, which can be seen upon close inspection. The gloss and brightness are slightly affected, but the overall quality is still good.
- Fair (F): The surface has obvious polishing marks, which can be detected under normal observation conditions. The luster and brightness are significantly affected, and the diamond's beauty is reduced.
- Poor (P): The surface has numerous obvious polishing marks, which are very easy to notice under normal observation conditions. The luster and brightness are significantly affected, greatly reducing the diamond's beauty.
Based on the polishing features visible at 10x magnification, multiple features need to be graded from excellent to poor.  The polish of a diamond is closely related to its cut grade. A high polish grade allows the diamond to reflect light to the maximum extent, thereby increasing its brilliance and fire.
The polish of a diamond is closely related to its cut grade. A high polish grade allows the diamond to reflect light to the maximum extent, thereby increasing its brilliance and fire.
6. Diamond symmetry
The symmetry of a diamond refers to whether the arrangement and proportions of its facets are perfectly symmetrical. Diamond symmetry is typically graded as follows : EX, VG, G, F, and P.
- Excellent (EX): The facets of the diamond are perfectly symmetrical, with no visible symmetry defects. This is the highest symmetry rating, indicating that the diamond's cut is extremely precise, maximizing light reflection for optimal brilliance and fire.
- Very Good (VG): The facets of the diamond are arranged very close to perfect symmetry, but there may be very few slight symmetry defects that can only be detected upon close inspection.
- Good (G): The diamond's facet arrangement has some noticeable symmetrical defects that can be observed under normal viewing. This has some impact on the diamond's optical properties, but overall it still has good brilliance and fire.
- Fair (F): The facets of this diamond have numerous symmetrical defects, which are easily noticeable under normal observation conditions. Optical properties are significantly affected, with a marked reduction in brilliance and fire.
- Poor (P): The diamond's facets exhibit numerous and easily noticeable symmetrical defects. Optical properties are severely impaired, significantly reducing the diamond's brilliance and fire.

Symmetry is one of the important indicators of diamond cut quality. Together with polish and cutting proportions, it determines the overall cut grade of a diamond.
7. Diamond fluorescence reaction - a design feature to counterfeit diamonds.
The fluorescence emitted by diamonds under strong UV light is similar to the fluorescent security features found in specific locations or patterns on banknotes. The GIA grades diamonds into five levels based on the intensity of the fluorescence they produce under UV light.

Because diamonds are affected by natural radiation during their formation, most diamonds fluoresce in blue. In rare cases, diamonds may emit white, yellow, green, or even red light. The different colors of fluorescence are determined by the diamond's crystal structure and its chemical composition.
Diamond grade and price
How to read a diamond price list?Step 1: Find the desired carat slot.
↓
Step 2: The horizontal column indicates diamond clarity, and the vertical column indicates color grade.
↓
Step 3: Find the corresponding field for the price per gram (USD) of this diamond grade.

The value of a diamond lies in the meaning we ourselves assign to it. Whether it symbolizes a small personal milestone, an engagement ring representing eternal love, or a family treasure to be passed down to future generations, diamonds are always closely linked to important moments in our lives. At different stages of life, everyone can own their own diamond to add brilliance to these precious moments.
Here are three different grades and prices of diamonds to meet different needs and budgets, so that each diamond can become an eternal memory for you.
"Recommended for beginners"
Carat: 0.3ct / Color: G / Clarity: VS2
The price is approximately: 1800 * 0.3 = US$540 ≈ TWD$17,000 
"Highly recommended for newlyweds"
Carat: 0.5ct / Color: F / Clarity: VS1
The price is approximately: 3000 * 0.5 = US$1500 ≈ TWD$49,000 
" Recommended for collectors"
Carat: 1ct / Color: F / Clarity: VVS1
The price is approximately: US$11,400 * 1 = TWD$370,000 
GIA Certificate - A Diamond's Identity Card
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) created the 4Cs standard, with particular emphasis on color and clarity.

Authenticity Certificate
Learning how to read a certificate and comparing it with the GIA grading certificate number and anti-counterfeiting marks is a crucial step in ensuring the authenticity of a diamond.
- Certificate Number:
- Each diamond certified by the GIA has a unique serial number.
- This number is usually laser-engraved on the girdle of the diamond.
- Use a magnifying glass or professional tools to examine the girdle of the diamond, find this number, and compare it with the number on the certificate.
- Anti-counterfeiting features:
- GIA certificates contain a variety of anti-counterfeiting features, such as watermarks, barcodes, and specific paper textures.
- Anti-counterfeiting watermarks are usually hidden in the background of the certificate and can be observed under light.
- The barcode can be verified through the GIA official website or a professional scanning tool.
- Online verification:
- Go to the GIA official website, access the "Report Check" function, enter the certificate number, and check if it matches the certification information on the website.
Master these tips to easily identify GIA diamond grading certificates and ensure the value of the diamonds you buy! ❅ ❅ ❅